Parallel Comparator (Flash) ADC
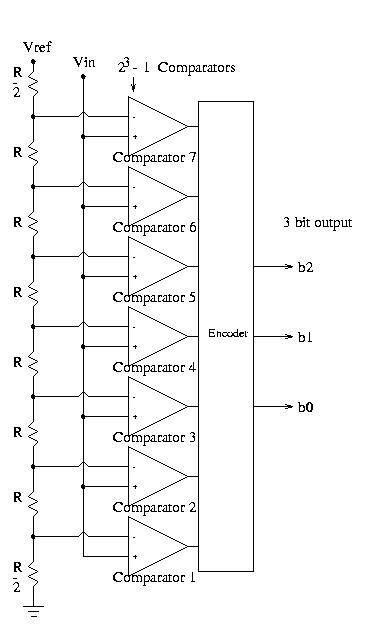
The flash ADC consists of 2n - 1 comparators where n is the number of output bits. The figure shows a flash ADC with 3 output bits, so 7 comparators are required. The comparator outputs behave like a bargraph with more of them outputting high, starting with comparator 1, as Vin is increased. If Vin is greater than Vref/14 than the output of comparator 1 will be high. If Vin is greater than 3Vref/14 than the output of comparator 2 will be high. Likewise, comparator 7 will be high for Vin > 13Vref/14. The encoder converts the bargraph type result to a binary representation, with output = 000 corresponding to all comparator outputs being low, and output = 111 meaning all comparator outputs are high.
An advantage of the flash ADC is that it is very fast, the disadvantage is the large number of comparators required. For example an 8 bit comparator requires 28 - 1 = 255 comparators. The number of comparators can be reduced by using the Subranging Parallel Comparator (Subranging Flash) ADC method.
